L,IFESTYLE
How to Identify Basic Electrical Wiring in AC ?
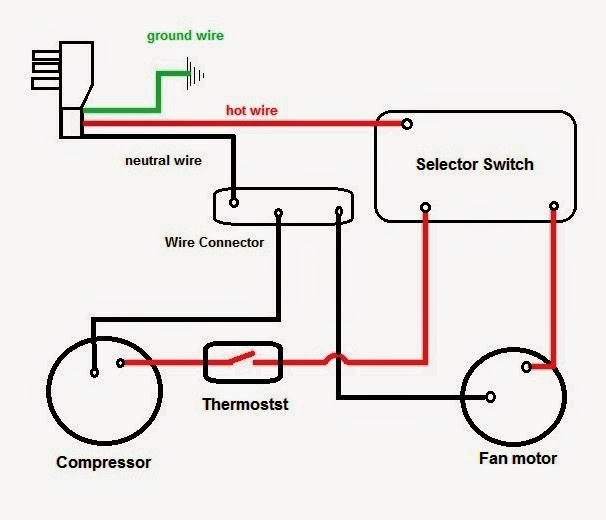
Understanding and effectively resolving electrical difficulties requires recognizing a fundamental electrical system. There are a handful of fundamental parts that make up the bulk of any electrical system. The first is access to electricity, which can come from a generator or the local power system.
The next part of a power system is the distribution panel, which is responsible for sending electricity to the various circuits in a building. For the more important information about the AC wiring and other problems like aircon not cooling, visit https://www.socool.sg/why-is-your-aircon-not-cold/
Electrical power sources, switches, and light fixtures are all linked to these circuits. The presence of these parts, as well as the condition of the wiring, the electrical boxes, and the switches and outlets, can be visually inspected to determine the existence of a basic electrical system. Knowing these basics sets the stage for competent and secure electrical use. To identify briefly the basic electrical wiring of AC, visit https://www.socool.sg/
1.The Power Source
A simple electrical setup cannot function without the power supply, which is an essential component. It supplies the power that is required for electrical equipment and appliances to function properly. Both the electrical grid, which receives power from a centralized power station, & generators, however, can produce electricity on the location where it is needed, are examples of common types of power sources.
Typically, the power source will be connected with the main control panel, which is the location where the electrical power will be transferred to the various circuits located throughout the structure.
2. The Distribution Panel
The distribution panel serves as the nerve center of the entire electrical network. It is responsible for obtaining electrical energy from the power sources and distributing that power to a number of different circuits using either fuses or circuit breakers.
By assisting in the avoidance of overloading and short-circuiting circuits, these protective devices contribute to the preservation of the integrity of the electrical network. In most homes, the utility room as well as basement is where one will find the distribution panel. This panel will have many breakers or fuses, each of which will be accountable for a separate circuit.
3. Circuits
Within a structure, electricity travels along circuits. Light switches, electrical outlets, and appliance plugs are all examples of things that normally have their own assigned uses. The distribution panel is where all the wires for the various circuits come together.
Copper or aluminum conductors are encased in insulation to avoid electrical shocks in the wiring. Circuits need to be properly labelled so that their function can be determined and repairs can be made more easily.
4. Outlets, switches and lightening features.
A fundamental electrical system must have outlets, switches, & lighting fixtures, all of which are considered to be vital components. The ability to connect various electrical appliances and devices to the circuits is made possible by outlets. Standard outlets, outlets equipped with ground-fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) for increased safety in areas close to water sources, and outlets designed specifically for a given use are all examples.
Lights and other electrical equipment can be turned on and off by using switches because switches regulate the flow of power to the gadgets. Lamps, bulbs, and other types of lighting fixtures are what give illumination in a variety of settings.
5. Wiring
It refers to the system of wires used to distribute current throughout a structure’s electrical infrastructure. The wiring links the power plant to the electrical panel and on to individual circuits, outlets, switches, & light fittings.
For safety and aesthetic reasons, wiring is often hidden within walls, ceilings, even conduits. ,nonmetallic sheathed cable armored cable (AC), and conduit wiring are just a few examples of the many types of electrical wiring that can be utilized based on the application and the applicable electrical rules.
6. Grounding and bounding
To ensure the safety of an electrical system, grounding and bonding must be properly implemented. In the case of an electrical malfunction or surge, grounding ensures that any excess current can safely drain into the ground. It’s an effective means of warding off electrical shocks and preserving machinery.
In order to reduce the possibility of electrical potential mismatches & electrical risks, connecting ensures that all conducting elements, which include metal pipes and appliances, are connected to one another. Electrodes, conductors, & bonding jumpers are the usual tools for grounding and bonding.
7. Safety measures
Essential to even the most fundamental electrical system are safety features like circuit breakers and regulations governing their installation and use. Overload and short circuit protection is achieved by installing circuit breakers or fuses, which cut power to the circuit when they detect an unsafe condition.
The danger of electrical risks can be reduced if installations are carried out in accordance with applicable electrical codes. If you want to make sure your home’s basic electrical system is running well, you need to have it checked, maintained, and follow all applicable safety measures.
L,IFESTYLE
Augie Martinez Lehigh: Transforming Student-Athletes with Leadership and Sports Excellence

Augie Martinez is a well-known name at Lehigh University, recognized for his contributions to sports and student development. His work in coaching and mentorship has shaped many student-athletes.
His journey at Lehigh goes beyond coaching, as he plays a crucial role in leadership development. Students under his guidance grow not just in sports but also in life skills.
The impact of Augie Martinez Lehigh is seen in the performance of teams and individual athletes. His methods focus on discipline, teamwork, and resilience.
From training programs to personal mentorship, his influence is widespread. His presence has strengthened Lehigh’s sports culture and continues to inspire future athletes.
Who is Augie Martinez Lehigh?
Augie Martinez is a highly respected figure at Lehigh University, known for his dedication to sports coaching and student mentorship. His leadership in athletics has helped many student-athletes develop both their skills and character.
Beyond coaching, Augie Martinez Lehigh plays a crucial role in guiding students toward success. His focus on discipline, teamwork, and perseverance has shaped Lehigh’s sports culture, making him an influential mentor and leader within the university.
Background and Early Career
Augie Martinez’s passion for sports started at a young age. His dedication to athletic excellence made him pursue a career in coaching.
Before joining Lehigh University, he built experience through various coaching roles. He developed a strong reputation for improving athlete performance.
His journey to Lehigh was shaped by his desire to help students reach their full potential. His expertise in training and mentorship became a valuable asset.
Throughout his career, he has emphasized teamwork and discipline. His leadership principles align perfectly with the values of Lehigh’s sports programs.
Role at Lehigh University
At Lehigh, Augie Martinez has taken on multiple roles, focusing on coaching and athlete development. His contributions extend beyond the field.
He works closely with student-athletes to improve their skills and strategies. His training programs are tailored to enhance both physical and mental strength.
In addition to coaching, he is involved in leadership initiatives. He helps students develop qualities like perseverance, teamwork, and confidence.
His role also includes fostering a winning mentality among athletes. Many students credit their success to his guidance and support.
Contributions to Athletics at Lehigh
Under Augie Martinez, Lehigh’s sports teams have shown remarkable improvement. His coaching has led to better performance and higher morale.
He believes in using modern techniques to train athletes. His approach includes strength training, strategy development, and psychological conditioning.
Key Achievements Under Augie Martinez:
- Improved team rankings in multiple sports.
- Higher individual performance levels in athletes.
- Enhanced team unity and discipline.
A strong emphasis is placed on long-term development. His coaching is not just about winning games but creating future leaders in sports.
Leadership and Mentorship at Lehigh
Martinez’s leadership is not limited to the sports field. He plays a crucial role in shaping young athletes into responsible individuals.
His mentorship programs focus on helping students balance sports and academics. He encourages athletes to stay dedicated to both their education and training.
Many students find inspiration in his guidance. His leadership style is motivational, disciplined, and encouraging.
Through his mentorship, students learn valuable life lessons. His influence prepares them for challenges beyond sports.
Community Engagement and Student Support
Beyond coaching, Augie Martinez Lehigh has contributed significantly to student development programs. He actively participates in university events and student initiatives.
His involvement in community service helps create a well-rounded student experience. He believes in giving back and encourages athletes to do the same.
Martinez is known for creating support networks for students. He ensures that athletes have access to the right resources for their growth.
Through workshops and training sessions, he teaches students the importance of discipline, respect, and perseverance. His impact extends beyond the university.
Challenges and Overcoming Obstacles
Every coach faces challenges, and Augie Martinez is no exception. Managing athlete expectations and team dynamics requires constant effort.
One of his biggest challenges has been balancing competitiveness with personal growth. He ensures that Lehigh athletes develop holistically, not just as players but as individuals.
Challenges in Coaching & How He Overcomes Them:
| Challenge | Solution Implemented |
| Team coordination | Focus on team-building exercises |
| Student stress & pressure | Mental conditioning programs |
| Injury management | Advanced recovery techniques |
His ability to solve problems effectively has made him one of Lehigh’s most respected sports leaders.
Legacy and Future Prospects
The influence of Augie Martinez will be felt at Lehigh University for years to come. His work has created a strong foundation for student-athletes.
Many students trained under him have gone on to achieve success in their respective sports. His mentorship has helped shape future leaders.
Looking ahead, his contributions will likely grow even further. As Lehigh’s sports culture continues to develop, his role will remain vital.
His dedication ensures that Lehigh remains a hub for athletic excellence. His work continues to inspire both current and future generations of students.
Conclusion
Augie Martinez is more than just a coach at Lehigh University. He is a mentor, leader, and motivator. His contributions have shaped the lives of many student-athletes.
Through his training programs, leadership initiatives, and mentorship, he has created a lasting impact. His work strengthens Lehigh’s reputation in athletics.
His influence is not only seen in sports but also in the character development of students. His ability to inspire makes him a valuable asset to the university.
The legacy of Augie Martinez Lehigh will continue to grow, making him an unforgettable figure in Lehigh’s sports history.
FAQs
Who is Augie Martinez at Lehigh University?
Augie Martinez is a respected coach and mentor at Lehigh University, known for his contributions to athletics and student development.
What is Augie Martinez’s role at Lehigh?
He plays a key role in coaching, leadership training, and mentoring student-athletes to enhance both their sports performance and personal growth.
How has Augie Martinez impacted Lehigh’s athletics?
His coaching has improved team rankings, athlete performance, and sports culture, fostering a strong sense of teamwork and discipline.
What makes Augie Martinez’s mentorship unique?
He focuses on holistic athlete development, teaching students important life skills alongside training for competitive success.
How does Augie Martinez support student success?
He provides training programs, leadership guidance, and mental conditioning, helping students balance sports and academics effectively.
ENTERTAINMENT
Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co: The Ultimate Growth Strategy for Brands

Luther is a leading name in the world of social media marketing. Known for his innovative strategies, he has helped businesses and influencers achieve significant growth. His expertise lies in understanding audience behavior and leveraging social trends effectively.
Keezy.co is the platform where Luther applies his marketing genius. It specializes in social media growth, brand engagement, and content strategy. Businesses looking to expand their online presence find Keezy.co to be a game-changer.
The platform’s success comes from a mix of advanced analytics and creative marketing. Luther ensures that brands connect with their audiences in meaningful ways. His approach is all about authenticity, engagement, and strategic planning.
Today, Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co is known for transforming small brands into digital powerhouses. Companies that struggle with low engagement and reach trust Keezy.co to provide effective solutions.
Who is Luther?
Luther is a social media maven, a title earned through years of expertise in digital marketing. He understands the ever-changing landscape of social media and stays ahead of trends. His ability to analyze and predict digital behavior makes him a top strategist.
His journey started with a passion for online engagement. Over time, he refined his skills in branding, marketing, and audience growth. Today, he works with businesses, influencers, and startups to elevate their social media presence.
Luther’s success is built on three core principles: authenticity, consistency, and strategic thinking. He believes that real engagement comes from genuine interactions rather than shortcuts. This mindset has helped Keezy.co establish its reputation as a trusted platform.
Through Keezy.co, he offers brands an opportunity to scale effectively. He not only helps them gain followers but also ensures that engagement translates into business growth.
The Rise of Keezy.co
Keezy.co was created to provide brands with a comprehensive social media growth solution. It started as a small idea but quickly evolved into a powerhouse for digital marketing. The platform focuses on organic growth, influencer collaborations, and content strategy.
Unlike many marketing platforms, Keezy.co prioritizes long-term success over quick fixes. Instead of relying on artificial engagement, it helps brands develop meaningful connections with their audience. This approach leads to higher trust and loyalty.
A key aspect of Keezy.co’s success is its data-driven decision-making. Luther ensures that every campaign is backed by analytics, tracking real-time performance. This allows brands to adjust strategies and maximize their online impact.
Today, Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co continues to grow as a preferred choice for businesses looking for sustainable social media success. The platform stands out due to its ability to combine creativity with data-driven precision.
What Keezy.co Offers?
Keezy.co provides a wide range of services that help brands grow their online presence. The platform specializes in tailored solutions, ensuring that businesses get strategies designed for their unique needs.
Key Services Offered by Keezy.co:
- Social Media Growth: Strategies to increase followers, engagement, and brand awareness.
- Influencer Collaborations: Connecting brands with the right influencers to boost visibility.
- Content Creation: High-quality posts, videos, and reels that captivate audiences.
- Data Analytics: Tracking campaign performance and optimizing strategies.
- Automation Tools: Streamlining posting, responses, and scheduling for efficiency.
These services make Keezy.co a valuable asset for any brand looking to dominate social media. The platform is designed to help businesses scale without relying on paid ads alone.
Luther’s expertise ensures that brands not only grow but also maintain their audience’s attention. His unique approach to digital marketing is what makes Keezy.co stand out in a competitive industry.
Luther’s Social Media Strategy
Luther’s approach to social media is different from traditional marketing. He focuses on building genuine relationships rather than chasing numbers. His strategy revolves around engagement, creativity, and adaptability.
The core of Keezy.co’s success lies in understanding audience behavior. By analyzing trends, Luther creates content that resonates with the target market. This ensures that brands don’t just get visibility but also meaningful interactions.
What Makes Luther’s Strategy Unique?
- Authenticity Matters: Brands grow faster when they stay true to their identity.
- Trends & Adaptation: Luther constantly updates strategies to align with changing algorithms.
- Quality Over Quantity: Instead of spam posting, he focuses on impactful content.
His expertise in multiple platforms, including Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter, allows brands to expand across different audiences. This multi-platform approach ensures maximum digital reach.
Why Keezy.co Stands Out?
Keezy.co is not just another marketing platform—it’s a full-scale social media growth solution. Unlike other services that rely on bots or paid ads, Keezy.co uses organic engagement strategies to build brand credibility.
One of the biggest strengths of Keezy.co is its ability to combine creativity with technology. Luther integrates AI-driven analytics to track performance while ensuring that content remains human and relatable.
The platform’s effectiveness can be seen in the results it delivers. Brands that use Keezy.co experience higher engagement rates, better audience retention, and stronger community building.
With its unique approach, Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co has positioned itself as a leader in digital branding and social media management. Businesses that partner with Keezy.co see long-term success instead of temporary spikes in engagement.
Success Stories & Case Studies
Many brands have benefited from Keezy.co’s expertise. From small startups to established companies, Keezy.co has helped businesses amplify their digital presence.
One of the most notable success stories includes a startup that grew from 5,000 to 100,000 Instagram followers in just six months. By using Keezy.co’s engagement strategies, the brand increased its sales by 40%.
Another case involved an influencer who struggled with engagement. After implementing Luther’s strategies, their content started reaching 10x more people, leading to brand partnerships and monetization opportunities.
These stories highlight the effectiveness of Keezy.co’s approach. Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co is not just about numbers—it’s about creating real impact.
Challenges & Future Goals
Despite its success, Keezy.co faces challenges in the constantly changing world of social media. Algorithm updates, competition, and audience behavior shifts require constant adaptation.
Luther stays ahead by analyzing trends and developing new strategies. His goal is to integrate more AI-powered tools and expand Keezy.co’s reach globally.
The future of Keezy.co includes more automation, deeper analytics, and expanded influencer marketing programs. Luther is always looking for ways to help businesses stay ahead in the digital race.
His ultimate vision is to make Keezy.co the go-to platform for sustainable social media growth. The focus will always remain on authenticity, engagement, and real business impact.
Conclusion
Luther has built Keezy.co into a powerful platform for social media growth. His expertise in digital marketing has helped countless businesses expand their online presence.
With authentic engagement, data-driven strategies, and innovative content marketing, Keezy.co offers solutions that drive real results.
Brands that want to scale their social media the right way can trust Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co. His strategies are built for long-term success, not just short-term spikes.
As the digital world evolves, Keezy.co continues to lead the way. With Luther’s expertise, businesses can navigate social media confidently and achieve sustainable growth.
FAQs
What makes Luther Social Media Maven Keezy.co different from other platforms?
Keezy.co focuses on organic engagement, AI-driven analytics, and influencer collaborations, ensuring long-term social media growth without shortcuts.
Can Keezy.co help small businesses grow on social media?
Yes, Keezy.co provides customized strategies to help small businesses increase followers, engagement, and brand visibility effectively.
Does Keezy.co use paid ads for social media growth?
No, Keezy.co prioritizes organic growth strategies like content optimization, influencer partnerships, and audience engagement for sustainable results.
How long does it take to see results with Keezy.co?
Growth timelines vary, but most clients see noticeable engagement improvements within 4 to 8 weeks using Keezy.co’s expert strategies.
Is Keezy.co suitable for influencers and personal brands?
Absolutely! Keezy.co helps influencers boost visibility, connect with audiences, and secure brand collaborations through effective marketing techniques.
ENTERTAINMENT
Sinpcity: The Ultimate Guide to Streaming, Gaming, and More

Sinpcity is a term that has multiple meanings across different industries. It is used to refer to a free streaming service, a video-sharing platform, a city-building game, an online adult forum, and even a travel destination.
Many people come across the word “Sinpcity” and assume it refers to a single entity. However, its usage varies widely depending on the context. Some associate it with entertainment, while others see it as a digital community.
The word has gained popularity due to its catchy and intriguing nature. It is commonly discussed on online forums, blogs, and social media platforms. Different industries have used the name to attract audiences looking for unique digital experiences.
Understanding the different interpretations of Sinpcity is essential for anyone trying to explore it. Whether it is about movies, gaming, or travel, knowing what Sinpcity stands for can help avoid confusion.
Origins of Sinpcity
The exact origin of the name Sinpcity is unclear, but it appears to be a play on words. Some believe it is a variation of “Sin City,” a term used to describe places known for their nightlife and entertainment.
Over time, the name has been adopted by various platforms to create a sense of excitement and intrigue. Streaming services, gaming companies, and online forums have used the name to appeal to different audiences.
The name may also be inspired by the cyber-world, where digital cities and online communities are common. Many internet-based platforms use creative names to establish their brand identity.
Sinpcity’s growing popularity suggests that it has become a recognizable term. Whether it refers to movies, gaming, or online content, it continues to attract attention from users worldwide.
Sinpcity as a Free Streaming Platform
One of the most well-known uses of Sinpcity is as a free streaming service. This platform allows users to watch movies and TV shows without advertisements or subscription fees.
It has gained a reputation for providing a vast library of content, including classic films, new releases, and popular TV series. Many users appreciate the ad-free experience, which sets it apart from other streaming platforms.
However, there are concerns about the legality and security of such services. Since Sinpcity offers free content, it is often questioned whether it operates within copyright laws. Users should always verify if the service is legal in their country.
Key Features of Sinpcity Streaming:
- Free access to a wide range of movies and shows
- No advertisements interrupting the viewing experience
- Available on different devices, including mobile and desktop
- Easy-to-use interface for quick navigation
Streaming platforms like Sinpcity continue to evolve, and their future depends on how they adapt to industry regulations and user demands.
Sinpcity as a Video-Sharing and Content Creation Platform
Another popular use of Sinpcity is as a video-sharing platform. Similar to YouTube, this version of Sinpcity allows creators to upload, share, and monetize their videos.
It provides a space for independent creators, vloggers, and educators to share their content with a global audience. Many users prefer this platform due to its user-friendly policies and creative freedom.
Monetization is an essential feature of this platform. Content creators can earn revenue through ad placements, sponsorships, and premium memberships. This makes it an attractive option for those looking to generate income from their videos.
Sinpcity’s success in the video-sharing industry depends on its ability to compete with established platforms. It must continue to innovate and provide unique tools for creators and viewers.
Sinpcity as a Virtual City-Building Game
Sinpcity is also known as a city-building simulation game. It allows players to design and manage their dream city, making decisions on infrastructure, economy, and public services.
Players can construct roads, buildings, and entertainment zones while ensuring that the city remains financially stable. The game challenges players to balance urban growth with resource management.
The competitive aspect of the game makes it more engaging. Some versions include multiplayer features where players can collaborate or compete to build the most successful city.
Gameplay Features of Sinpcity:
- Create and customize cities with different themes
- Manage resources such as water, electricity, and transportation
- Engage in city politics and economic strategies
- Compete with other players in multiplayer modes
As city-building games continue to attract players, Sinpcity stands out for its immersive experience and strategic depth.
Sinpcity as an Adult Forum
Another interpretation of Sinpcity refers to an online adult forum, sometimes discussed under the name Simpcity.su. This forum has been known for hosting controversial content.
Users visit such forums to share explicit material, discuss adult topics, and engage in online interactions. However, these platforms often face legal and ethical issues.
Privacy and security concerns are significant when using such forums. Since they operate in a legal gray area, users risk exposure to data leaks or legal actions.
Many of these forums have been taken down or restricted in certain regions due to legal concerns. It is crucial to research before engaging with such platforms.
Sinpcity as a Travel Destination
Some travel blogs refer to Sinpcity as a vibrant location known for its nightlife, entertainment, and scenic views. These destinations attract tourists looking for excitement and adventure.
Sinpcity-style cities are known for their lively atmosphere, casinos, luxury hotels, and cultural attractions. They offer a mix of modern entertainment and historical sites.
Popular Attractions in Sinpcity-Like Destinations:
- Famous casinos and nightlife spots
- Stunning architecture and cityscapes
- Gourmet restaurants and fine dining experiences
- Unique festivals and events
Travelers visiting such places should explore both well-known attractions and hidden gems to get the full experience. Sinpcity-style destinations continue to draw millions of visitors every year.
Common Misconceptions About Sinpcity
Many people misunderstand what Sinpcity refers to. Some assume it is just a movie streaming site, while others think it is only a gaming platform.
Due to its multiple interpretations, people often confuse different versions of Sinpcity. This can lead to misinformation when searching for specific content related to it.
Some users also believe that Sinpcity is an illegal service. While certain versions operate in legal gray areas, not all platforms under this name are illegal.
Understanding the different meanings of Sinpcity helps in finding the correct platform or service. Doing proper research is essential before using or engaging with any version of Sinpcity.
The Future of Sinpcity
The future of Sinpcity depends on how it continues to evolve in different industries. Streaming services, gaming, and digital platforms must adapt to changing trends and legal regulations.
As competition increases, Sinpcity platforms must offer better services to attract users. The streaming industry, for example, must ensure compliance with copyright laws.
Gaming platforms will likely introduce more advanced features, such as AI-driven city-building tools and interactive multiplayer experiences. The demand for engaging digital content will drive innovation.
In the coming years, Sinpcity might expand into new areas, including virtual reality and blockchain technology. Its evolution will depend on how well it adapts to future market trends.
Conclusion
Sinpcity is a term that has multiple meanings, ranging from entertainment to gaming and online forums. Its diverse usage makes it a popular but sometimes misunderstood name.
Whether referring to a streaming platform, a content-sharing site, or a virtual game, Sinpcity continues to attract attention. Each version has its own set of advantages and challenges.
As technology advances, Sinpcity will likely evolve to meet the needs of modern users. Those interested in Sinpcity should explore its different aspects to understand which one suits their interests.
By staying informed, users can make better decisions on how they engage with Sinpcity-related platforms in the future.
FAQs
What is Sinpcity best known for?
Sinpcity is known as a free streaming platform, a video-sharing site, a city-building game, an adult forum, and a travel destination.
Is Sinpcity a legal streaming service?
Some versions operate legally, but others may offer content without proper licensing, so users should verify their region’s copyright laws.
Can I earn money on Sinpcity’s video-sharing platform?
Yes, content creators can monetize their videos through ads, sponsorships, and premium memberships, similar to YouTube.
How does the Sinpcity game compare to SimCity?
Sinpcity offers similar city-building mechanics but often includes unique customization, multiplayer options, and economic challenges.
Is Sinpcity a real place for travel?
Some cities with vibrant nightlife and entertainment are called “Sinpcity,” though no official destination exists under this name.
-

 L,IFESTYLE2 years ago
L,IFESTYLE2 years agoExploring the Heart of Iowa City Downtown District
-

 TECH2 years ago
TECH2 years agoMaximizing Your Pixel 6a’s Wireless Charging Performance: Tips and Tricks
-

 SPORTS3 years ago
SPORTS3 years agoclub america vs deportivo toluca f.c. timeline
-
CRYPTO2 years ago
Features of Liquidity Providers and Differences Between Them
-

 BUSINESS2 years ago
BUSINESS2 years agoThe Evolution of the Patagonia Logo: A Look at the Brand’s Iconic Emblem
-
 TECH3 years ago
TECH3 years agoBuild Your Email Marketing Contact
-
 TECH3 years ago
TECH3 years ago6 Ways AI Will Change the Future of Marketing
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoProstavive Colibrim: A Natural Prostate Health Supplement









